Want to Know about E-Way Bill in detail?
1. What is an E-Way Bill?
E-Way Bill is the short form of Electronic Way Bill. It is a unique document/bill, which is electronically generated for the specific consignment/movement of goods from one place to another, either inter-state or intra-state.
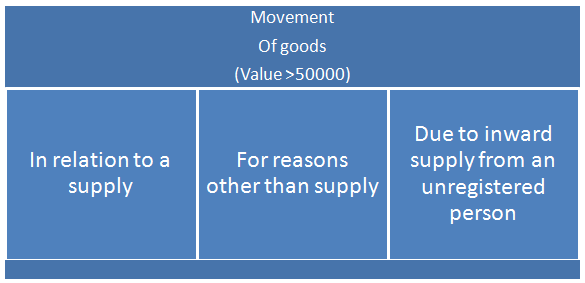
The e-way Bill System for Inter-State movement of goods across the country has been introduced from 01 April 2018. E-Way Bill is mandatory for Inter-State movement of goods of consignment value exceeding INR 50,000, in motorized conveyance under the current GST regime.
2. E-Way Bill under GST
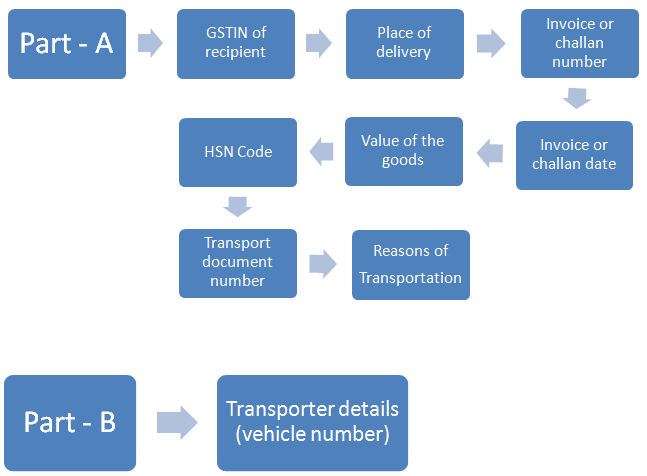
The bill comprises of 2 parts – Part A and Part B.
3. Who should generate an e-way bill?
GST Registered Person:
(a) When a registered person causes the movement of goods/ consignment, either in the capacity of a consignee (i.e., buyer) or consignor (i.e., seller) in his/her vehicle or hired vehicle or railways or by air or by ship, then either the registered person or the recipient should generate the e-Way Bill in Form GST EWB 01 electronically on the common portal by furnishing information in Part B.
(b) When a registered person causes the movement of goods and hands these over to the transporter for transportation by road, but the e-Way Bill has not been generated, then it is the transporter who needs to generate the bill. The registered person will first furnish the information relating to the transporter in Part B of Form GST EWB. After this, the transporter will generate the e-Way Bill by the information furnished by the registered person through Part A of Form GST EWB 01.
Unregistered Person:
(a) When an unregistered person causes the movement of goods, through his/her conveyance or hired conveyance or using the services of a transporter, then the e-Way Bill needs to be generated either by the unregistered person or by the transporter, by completing Form GST EWB-01.
(b) When an unregistered person supplies the goods to a registered person AND the registered person is known to the unregistered person at the time of the start of the movement of goods, then it will be considered that the registered person is moving the consignment. In this case, the registered person or transporter shall complete the formalities of the e-Way Bill.
4. When should the e-way bill be generated?
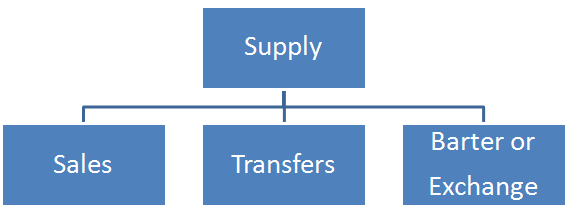
Supply may be either of the following:
- A supply made for a consideration (payment) in the course of business.
- A supply made for a consideration (payment) which may not be in the course of business.
- A supply without consideration (without payment).
èIn simpler terms, supply usually means:
èA special situation where e-way bills must be issued on the common portal even if the value of the consignment of Goods is less than Rs.50,000.
5. E-WAY BILL EXEMPTION
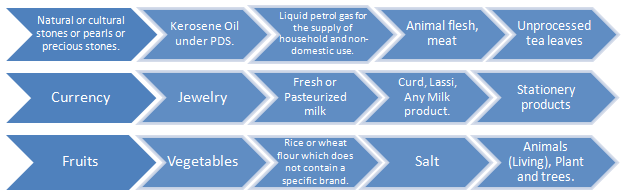
There are specific goods and transactions which do not require E Way Bill and are exempted from the generation of E Way Bill.
Exemption for Goods:
Exemption for Transactions:
- Generation of E Way Bill is not mandatory for the goods which are below the threshold of 50000 rupees and being transported from one place to another.
- In case the goods are transferred by Non - motorized vehicles.
- If the port, airport, air cargo complex, and land customs station to an inland container depot (ICD) or a container freight station (CFS) for clearance by Customs.
- Goods transported within the area which is notified.
- Goods that are transported to the Ministry of Defense.
6. The validity period of the e-way bill:
An e-way bill is valid for periods as listed below, which is based on the distance traveled by the goods.
|
Sr.No. |
Distance within country |
Validity period of relevant date* |
|
1 |
Up to 100 km |
One day in cases other than Over Dimensional Cargo** |
|
2 |
For every 100 km or part thereof thereafter |
One additional day in cases other than Over Dimensional Cargo |
|
3 |
Up to 20 km |
One day in cases of Over Dimensional Cargo |
|
4 |
For every 20 km or part thereof thereafter |
One additional day in cases of Over Dimensional Cargo |
*Relevant date means the date on which e-way bill has been generated and the period of validity shall be counted from the time at which e-way bill has been generated and each day shall be counted as a period of expiring at midnight of the day immediately following the date of generation of e-way bill.
**Over dimensional cargo means a carried as a single indivisible unit and which exceeds the dimensional limits prescribed in rule 93 of the Central Motor Vehicles Act, 1988.
7. Extension of the validity period
èExtension by Commissioner for certain categories of goods:
Commissioner may, on the recommendation of the Council, by notification, extend the validity period of an e-way bill for certain categories of goods as may be specified therein.
èExtension by the transporter in exceptional circumstances:
Where under circumstances of exceptional nature, including trans-shipment, the goods cannot be transported within the validity period of the e-way bill, the transporter may extend the validity period after updating the details in Part B, if required. The transporter can extend the validity of the e-way bill, if the consignment is not being reached the destination within the validity period due to exceptional circumstances like natural calamity, law, and other issues, trans-shipment delay, an accident of conveyance, etc. He needs to explain this reason in detail while extending the validity period. This option is available for extension of an e-way bill before 8 hours & after 8 hours of expiry of the validity.
8. Acceptance of e-way bill
The details of the e-way bill generated shall be made available to the –
- Supplier, if registered, where the information in Part A has been furnished by the recipient/transporter.
- Recipient, if registered, where the information in Part A has been furnished by the supplier/transporter.
On the common portal and the supplier/recipient, as the case may be, shall communicate his acceptance or rejection of the consignment covered by the e-way bill [Rule 138(11)].
In case, the person to whom the information in Part-A is made available does not communicate his acceptance or rejection within a specified time; it shall be deemed that he has accepted the said details. The time-limit specified for this purpose is:
- 72 hours of the details being made available to him on the common portal.
- The time of delivery of goods.
Whichever is earlier.
9. Cancellation of e-way bill
Where an e-way bill has been granted, but goods are either not transported or are not transported as per the details furnished in the e-way bill, the e-way bill may be canceled electronically on the common portal within 24 hours of generation of the e-way bill.
However, an e-way bill cannot be canceled if it has been verified in transit under the provisions of the rule 138B.
Further, the unique EWB number generated is valid for 15 days for updation of Part B.
10. Documents to be carried by person-in-charge of a conveyance
- Invoice or a bill of supply or delivery challan
- Copy of the e-way bill in physical bill number in electronic form.